Kirnberger Temperament on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Kirnberger temperament is an irregular
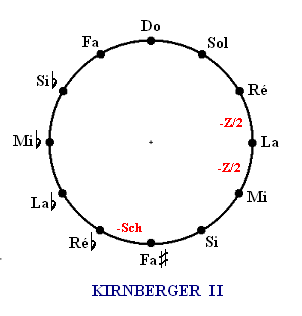 Kirnberger's first method of compensating for and closing the circle of fifths was to split the "
Kirnberger's first method of compensating for and closing the circle of fifths was to split the "
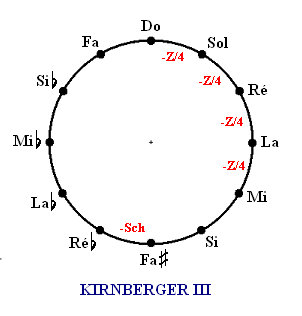 After some disappointment with his sour, narrow fifths, Kirnberger experimented further and developed another possibility, later named the Kirnberger III.
This temperament splits the
After some disappointment with his sour, narrow fifths, Kirnberger experimented further and developed another possibility, later named the Kirnberger III.
This temperament splits the
temperament
In psychology, temperament broadly refers to consistent individual differences in behavior that are biologically based and are relatively independent of learning, system of values and attitudes.
Some researchers point to association of temperam ...
developed in the second half of the 18th century by Johann Kirnberger. Kirnberger was a student of Johann Sebastian Bach
Johann Sebastian Bach (28 July 1750) was a German composer and musician of the late Baroque period. He is known for his orchestral music such as the '' Brandenburg Concertos''; instrumental compositions such as the Cello Suites; keyboard wo ...
, held great admiration for his teacher and was one of his principal proponents.
The first Kirnberger temperament, "Kirnberger I", had similarities to Pythagorean temperament, which stressed the importance of perfect fifths all throughout the circle of fifths
In music theory, the circle of fifths is a way of organizing the 12 chromatic pitches as a sequence of perfect fifths. (This is strictly true in the standard 12-tone equal temperament system — using a different system requires one interval of ...
. A complete circle of perfect fifths is not possible, because when the circle comes to an end at the tone it began, it will have overshot its original pitch. Thus, if one tunes C–G, G–D, D–A, A–E, E–B, B–F, F–C, C–G (A), A–E, E–B, B–F, F–C … the new "C" will not be the same frequency as the first. The two "C"s will have a discrepancy of about 23 cents (a comma), which would be unacceptable. This difference between the initial "c" and final "c" that is derived from performing a series of perfect tunings is generally referred to as the ''Pythagorean comma
In musical tuning, the Pythagorean comma (or ditonic comma), named after the ancient mathematician and philosopher Pythagoras, is the small interval (or comma) existing in Pythagorean tuning between two enharmonically equivalent notes such as ...
''. In Kirnberger I, the D–A fifth is reduced by a syntonic comma
In music theory, the syntonic comma, also known as the chromatic diesis, the Didymean comma, the Ptolemaic comma, or the diatonic comma is a small comma type interval between two musical notes, equal to the frequency ratio 81:80 (= 1.0125) ...
, making the major thirds F–A, C–E, G–B, and D–F# pure, though the fifth based on D is a ratio of 40/27 instead of 3/2. Many tuning systems have been developed to "spread around" that comma, that is, to divide that anomalous musical space among the other intervals of the scale.
Practical Temperaments: Kirnberger II
wolf
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, and gray wolves, as popularly un ...
" interval, known to those who have used meantone
Meantone temperament is a musical temperament, that is a tuning system, obtained by narrowing the fifths so that their ratio is slightly less than 3:2 (making them ''narrower'' than a perfect fifth), in order to push the thirds closer to pure. Me ...
temperaments, in half between two different fifths. That is, to compensate for the one extra comma, he removed half a comma from two of the formerly perfect fifths in order to complete the circle. In so doing, he allowed the remaining fifths to stay pure. At the time, however, pure thirds were more valued than pure fifths (meantone temperament had eight pure thirds and sacrificed four entire chords to achieve this end.) So, Kirnberger allowed for three pure thirds, the rest being slightly wide and the worst being three Pythagorean
Pythagorean, meaning of or pertaining to the ancient Ionian mathematician, philosopher, and music theorist Pythagoras, may refer to:
Philosophy
* Pythagoreanism, the esoteric and metaphysical beliefs purported to have been held by Pythagoras
* Ne ...
thirds (22 cents wider than pure) on the opposite end of the circle from the pure thirds. To put it graphically:
C-----G-----D------A-----E-----B-----F#-----C#-----Ab(G#)-----Eb-----Bb-----F-----C
p p −1/2 −1/2 p p p p p p p p
, __________pure 3rd______,
, __________pure 3rd______,
, _______pure 3rd________,
, __________Pythag. 3rd_________,
, _________Pythag. 3rd___________,
, ________Pythag. 3rd___________,
The above table represents Kirnberger II temperament. The first row under the intervals shows
either a "p" for pure, or "−1/2" for those intervals narrowed to close the circle of fifths (D–A), (A–E). Below these are shown the pure 3rds (between C–E, G–B, D–F), and Pythagorean (very wide) 3rds (B–D, F–A(B), D–F.)
Temperament, however, is a give-and-take situation: none is a perfect solution. It must also be remembered that temperament applies only to instruments with fixed pitch: any keyboard instrument, lutes
A lute ( or ) is any plucked string instrument with a neck and a deep round back enclosing a hollow cavity, usually with a sound hole or opening in the body. It may be either fretted or unfretted.
More specifically, the term "lute" can re ...
, viols
The viol (), viola da gamba (), or informally gamba, is any one of a family of bowed, fretted, and stringed instruments with hollow wooden bodies and pegboxes where the tension on the strings can be increased or decreased to adjust the pitc ...
, and so forth. Wind musicians, singers and string players all have a certain degree of flexibility concerning the exact pitch and intonation of what they play and may therefore be free of such restrictive systems. When the two classes of players come together, it is important when evaluating a temperament to consider the tendencies of the instruments vs. those of the temperament. Kirnberger II would only have been applicable to keyboard instruments such as the harpsichord and organ. The advantages of this system are its three pure major thirds and its ten pure fifths; the disadvantages are, of course, the two narrow "half-wolf" fifths and the three Pythagorean, super-wide thirds. The chords are not unusable but certainly must not be used frequently or in close succession within the course of a piece.
Kirnberger III
Syntonic comma
In music theory, the syntonic comma, also known as the chromatic diesis, the Didymean comma, the Ptolemaic comma, or the diatonic comma is a small comma type interval between two musical notes, equal to the frequency ratio 81:80 (= 1.0125) ...
between four fifths instead of two. 1/4-comma tempered fifths are used extensively in meantone
Meantone temperament is a musical temperament, that is a tuning system, obtained by narrowing the fifths so that their ratio is slightly less than 3:2 (making them ''narrower'' than a perfect fifth), in order to push the thirds closer to pure. Me ...
and are much easier to tune and to listen to. This also eliminates two of the three pure thirds found in Kirnberger II. Therefore, only one third remains pure (between C and E), and there are fewer Pythagorean thirds. A greater middle ground is thus reached in this improvement, and each key is closer to being equal to the next. The drawback is an aesthetic one: fewer chords have pure thirds and fifths. But every temperament system has a give-and-take compromise; each has to find a way of dealing with the comma.
See also
*Friedrich Wilhelm Marpurg
Friedrich Wilhelm Marpurg (21 November 1718 – 22 May 1795) was a German music critic, music theorist and composer. He was friendly and active with many figures of the Enlightenment of the 18th century.
Life
Little is known of Marpurg's ear ...
*'' Construction der gleichschwebenden Temperatur''
Further reading
*Klop, G.C. (1974) ''Harpsichord Tuning''. The Sunbury Press, Raleigh, N.C. Designated "Kirnberger 2"Lieberman and Miller (2006). ''Lou Harrison'', p.80. . and presumably other Kirnberger temperaments. * Willem Kroesbergen, Andrew Cruickshank "18th century quotes on J.S. Bach's Temperament (2014) https://www.academia.edu/5210832/18th_Century_Quotes_on_J.S._Bach_s_Temperament * Dominic Eckersley "Rosetta Revisited" https://dominiceckersley.files.wordpress.com/2013/04/rosetta_revisited.pdfSources